MariaDB is an open-source, multi-threaded relational database management system. Commonly used for LAMP (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) or LEMP (Linux, Nginx, MariaDB, PHP). MariaDB gains popularity after Linux distro adopted MariaDB as the default replacement for MySQL due licensing issue.
MariaDB 10.5 new features
– Includes the S3 storage engine
– MariaDB ColumnStore storage engine
– New Gamma version of the Spider Storage Engine
In this tutorial, we’ll run MariaDB on a single server, which commonly used for small to medium websites. We’ll cover how to clustering MariaDB in the next tutorial.
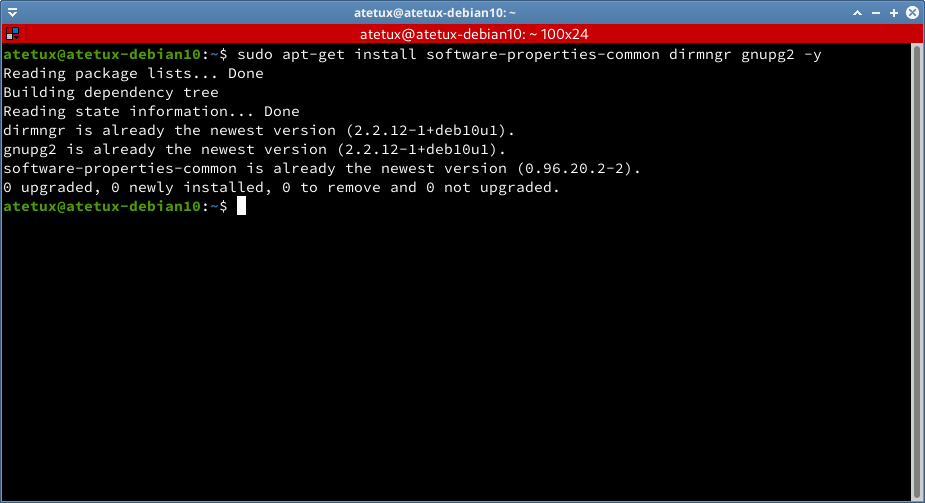
Install Dependency
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common dirmngr gnupg2 -y
Add MariaDB Repository
Add MariaDB 10.5 repository, and install signing key
sudo add-apt-repository 'deb [arch=amd64] http://sgp1.mirrors.digitalocean.com/mariadb/repo/10.5/debian buster main' sudo apt-key adv --fetch-keys 'https://mariadb.org/mariadb_release_signing_key.asc'
Update Repository
Every time apt repository changes, we must update the metadata
sudo apt updateInstall MariaDB 10.5
Finally install MariaDB 10.5 using apt
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server -y
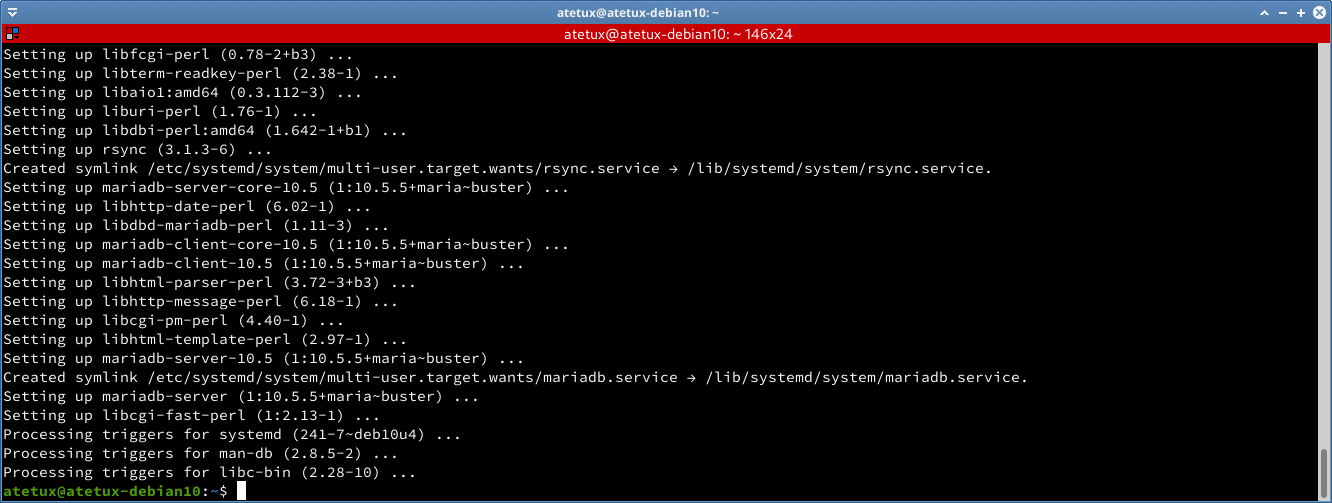
on Debian every application installed using apt running automaticly.
Run MariaDB on Booting
To make sure every time system booting MariaDB run automaticly run following command
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
Check MariaDB Services
Check the MariaDB services
sudo systemctl status mariadb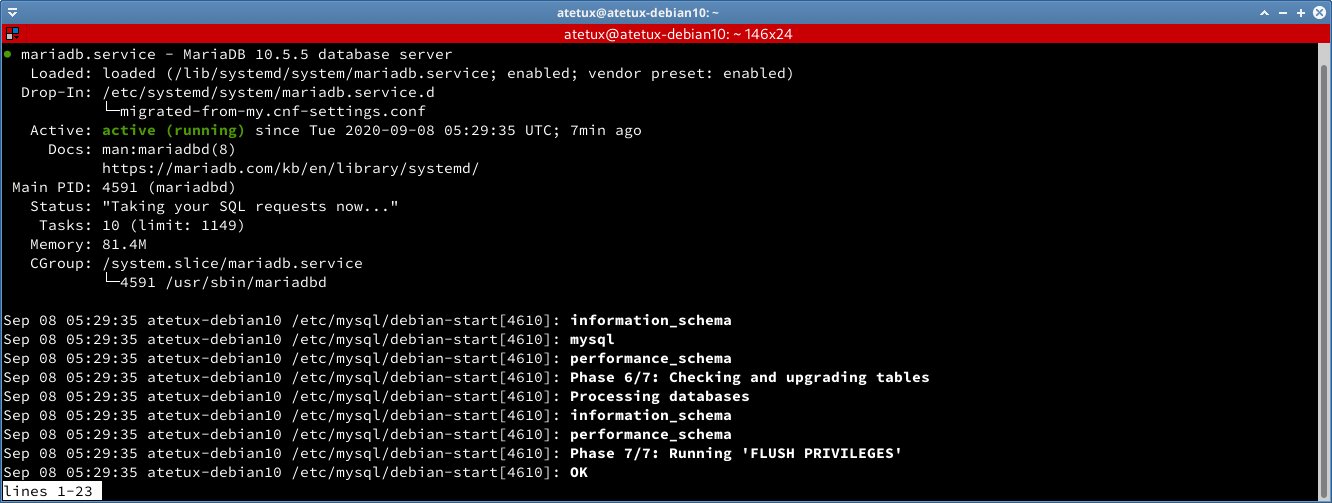
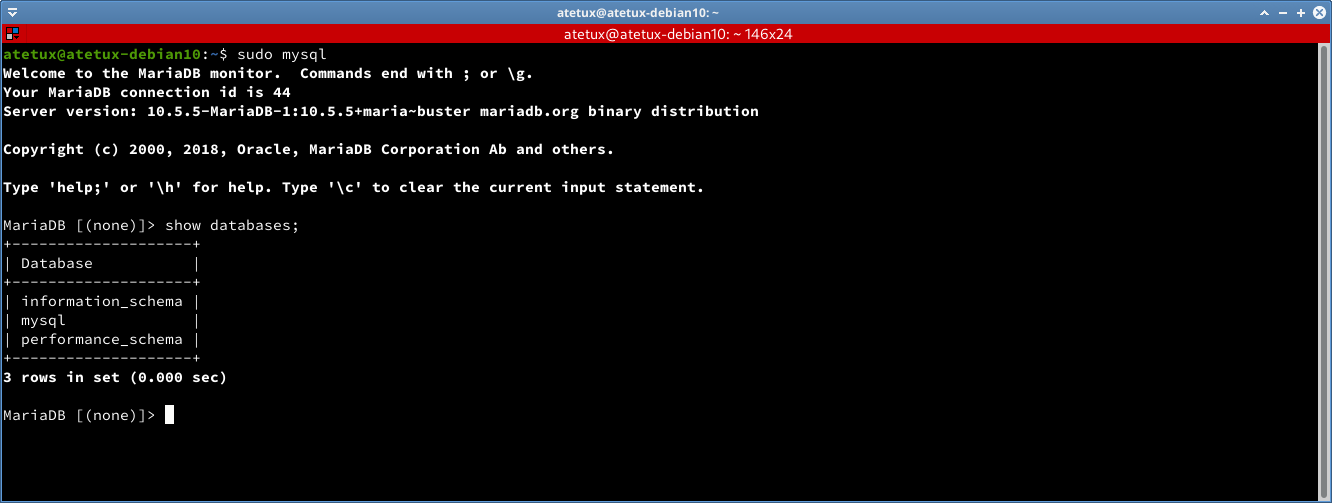
Next login to MySQL as root, to run some query
sudo mysql