Minikube is a defacto for testing Kubernetes on the local computer. It has all the basic features from Kubernetes, and it’s raw, no plugin or customized feature added. So if it’s working on Minikube, it should run on managed Kubernetes engines like Google Kubernetes Engine, Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) etc with minimal config changes.
Alternative for Minikube are k3s, microk8s, k0s.
Minimum Requirement System
Minimum requirement system for Minikube
4 GB memory
2 CPU
10 GB Disk (SSD Prefered)
it’s the minimum, so your computer should have more memory because we run another application other than Minikube itself. My computer had 32 Memory, so I have plenty memory left for Minikube.
Initial Setup
This initial setup will help to speed up the installation process because we install the dependency first. It should not throw any dependency error later on.
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release wget
Install Cloud Tools
These cloud tools are basically what we need to manage the Kubernetes cluster. Depending on your need, you may need to install more tools, but for a basic or beginner, it should be enough as a starting point.
1. kubectl
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
2. helm
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.8.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz tar zxvf helm-v3.8.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
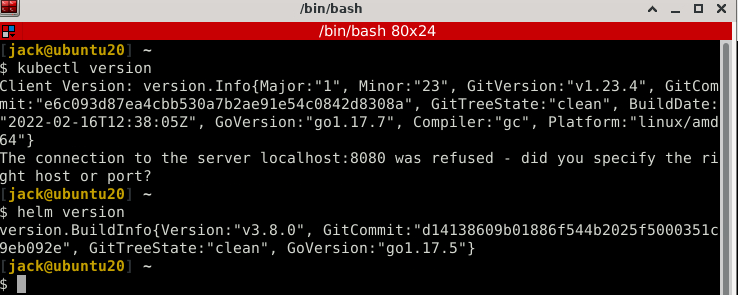
Verify the tools working by running command
kubectl version helm version
Install Docker
For the docker itself, use the docker from official docker repository, it’ll always updated when new release coming. So for development it’s really important to test on the latest version.
Install the latest version of docker from docker apt repository
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null sudo apt update sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
Verify installed version
docker --version # output Docker version 20.10.12, build e91ed57
To able run the docker by a normal user, add docker group to your current user
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER # verify id $USER
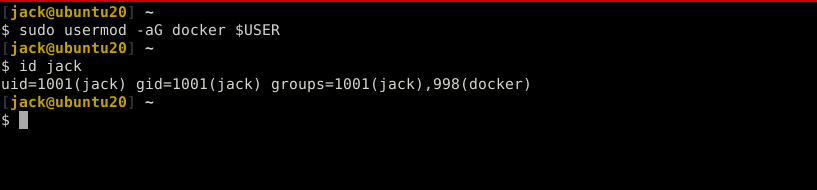
after adding a new group we need to log out and log in again. My preferred method is just to reboot
sudo rebootInstall Minikube
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
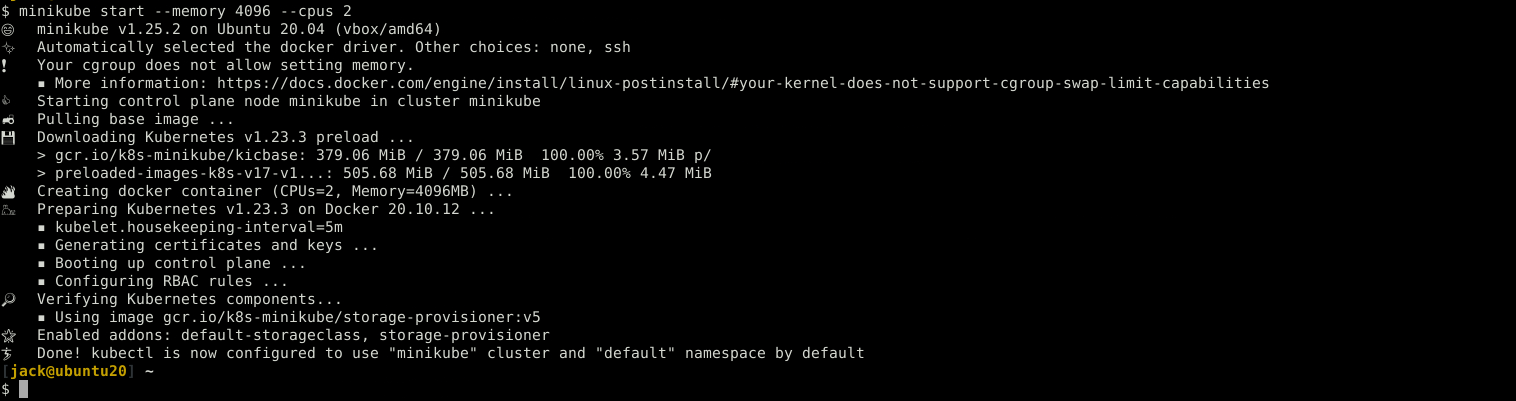
By default, minikube use 2 GB memory and 2 CPU, but for testing a lot of software or feature that won’t be enough, depend on your computer memory you can use 50% of available memory or more. We can customize this by running
minikube start --memory 4096 --cpus 2
it’ll use the latest version of Kubernetes, to use a specific version add --kubernetes-version=VERSION at the end of the command
# example minikube start --memory 4096 --cpus 2 --kubernetes-version=v1.20.1
Check the kubernetes using kubectl
kubectl get ns
# output
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 5m4s
kube-node-lease Active 5m6s
kube-public Active 5m6s
kube-system Active 5m6sPull from docker registry and run busybox pod on your cluster
kubectl run busybox --image=busybox --command sleep infinity
that pod will run forever, because we add sleep infinity. It’ll helpful for debugging
Minikube with local Docker Images
Create a simple docker image, using nginx as a base image. Everytime use run/visit the docker image, it’ll return ‘Atetux local docker’. Create new folder for our little project
mkdir -p ~/docker/nginx-custom cd ~/docker/nginx-custom
create new file for index.html
echo 'Atetux local docker' > index.html
create new file Dockerfile
FROM nginx COPY index.html /usr/share/nginx/html/
the build the docker image
docker build . -t nginx-atetux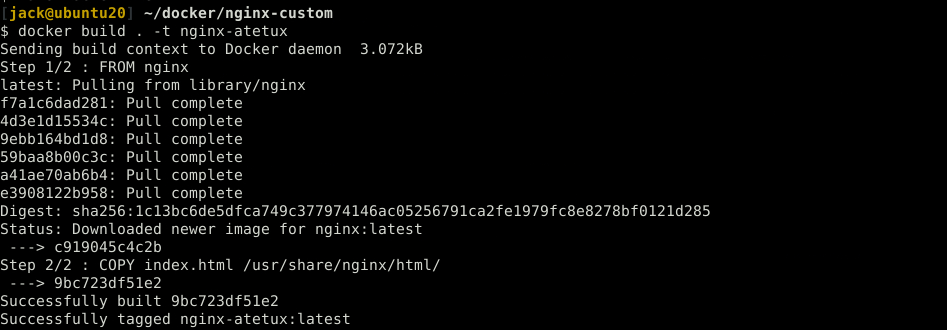
After the build finish, deploy it to kubernetes
kubectl run nginx-atetux --image=nginx-atetux:latest --image-pull-policy=IfNotPresent
for some reason you won’t be able to download the images
kubectl get pods # output nginx-atetux 0/1 ErrImagePull 0 46s
That is because your local docker and minikube docker run on the different daemon.
To able deploying docker from your local docker, run the command below to use minikube docker daemon instead of your docker
eval $(minikube -p minikube docker-env)
build the image again
docker build . -t nginx-atetuxcheck the pod again, it should be on running condition
kubectl get pods # output nginx-atetux 1/1 Running 0 4m21s
to verify this is working, both of these commands should give the same output
minikube image list docker images