Fluentbit is created as a fluentd successor for cloud native, which use less memory and faster to process the logs. To make is easy managing fluentbit in Kubernetes, like update the config, reload the pod, etc we’ll use fluent-operator.
Let’s setup the fluent-operator from scratch.
Deploy fluent-operator and fluentbit
To deploy fluent-operator and fluent bit, we’ll use helm. Which is more easy to customize and install to Kubernetes cluster.
Depend on your use case, it’s might better to create a dedicated namespace for monitoring tools, as an example we’ll create namespace called monitoring
kubectl create namespace monitoring
Add new repo to deploy from fluent which include fluent bit and fluent operator.
git clone https://github.com/fluent/fluent-operator.git cd fluent-operator
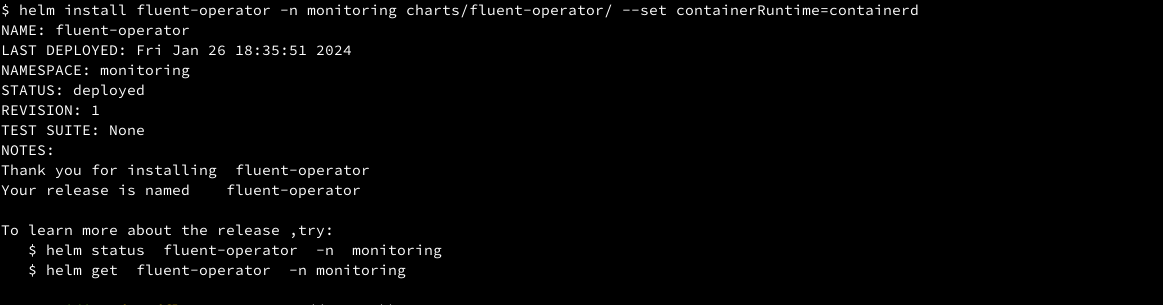
Install fluent-operator
helm install fluent-operator -n monitoring charts/fluent-operator/ --set containerRuntime=containerd
fluent operator will manage the fluentbit config via CRD. For upgrade the fluentbit chart, beware `helm upgrade –install` didn’t upgrade the CRD, you need to install the CRD using `kubectl`
kubectl get clusterfluentbitconfigs.fluentbit.fluent.io,clusterfluentbitconfigs,clusterinputs.fluentbit.fluent.io,clusterfilters.fluentbit.fluent.io,clusteroutputs.fluentbit.fluent.io,clusterparsers.fluentbit.fluent.io -n monitoring # output NAME AGE fluent-bit-config 77s NAME AGE clusterinput.fluentbit.fluent.io/containerd 77s clusterinput.fluentbit.fluent.io/tail 77s NAME AGE clusterfilter.fluentbit.fluent.io/containerd 77s clusterfilter.fluentbit.fluent.io/kubernetes 77s clusterfilter.fluentbit.fluent.io/systemd 77s
Check the pods in monitoring namespace
$ kubectl get pods -n monitoring NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE fluent-bit-d8llc 1/1 Running 0 50s fluent-operator-5df64cb5b9-k7wb2 1/1 Running 0 4m25s
All values from custom resources above, will stored as secret, which will used by fluentbit pod. To get the config, run following command
kubectl get secret/fluent-bit-config -o json -n monitoring | jq -r '.data."fluent-bit.conf"' | base64 -d
output
[Service] Http_Server true Parsers_File parsers.conf [Input] Name systemd Path /var/log/journal DB /fluent-bit/tail/systemd.db DB.Sync Normal Tag service.* Systemd_Filter _SYSTEMD_UNIT=docker.service Systemd_Filter _SYSTEMD_UNIT=kubelet.service Strip_Underscores off storage.type memory [Input] Name tail Path /var/log/containers/*.log Read_from_Head false Refresh_Interval 10 Skip_Long_Lines true DB /fluent-bit/tail/pos.db DB.Sync Normal Mem_Buf_Limit 100MB Parser docker Tag kube.* storage.type memory [Filter] Name lua Match kube.* script /fluent-bit/config/containerd.lua call containerd time_as_table true [Filter] Name kubernetes Match kube.* Kube_URL https://kubernetes.default.svc:443 Kube_CA_File /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt Kube_Token_File /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token K8S-Logging.Exclude true Labels true Annotations false [Filter] Name nest Match kube.* Operation lift Nested_under kubernetes Add_prefix kubernetes_ [Filter] Name modify Match kube.* Remove stream Remove kubernetes_pod_id Remove kubernetes_host Remove kubernetes_container_hash [Filter] Name nest Match kube.* Operation nest Wildcard kubernetes_* Nest_under kubernetes Remove_prefix kubernetes_ [Filter] Name lua Match service.* script /fluent-bit/config/systemd.lua call add_time time_as_table true [Output] Name stdout Match *
Enable Debug Mode
debug mode really helpful to troubleshooting issue in fluent-bit or plugin in general, it produces a lot more information. Don’t enable this on production, because it’ll generate a lot of garbage logs which not related to your Kubernetes cluster.
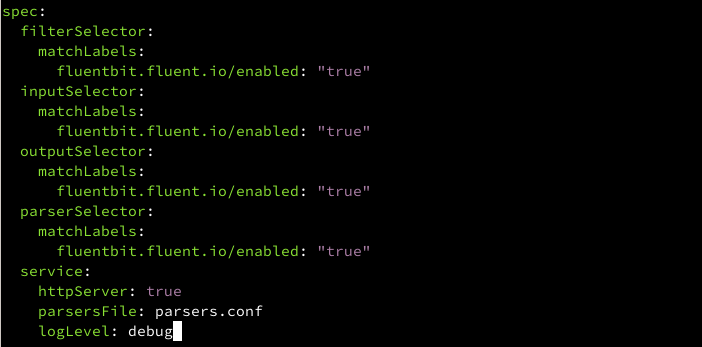
Fluentbit use clusterfluentbitconfigs object to store the Service config, let’s update it
kubectl edit clusterfluentbitconfigs.fluentbit.fluent.io/fluent-bit-configafter parsersFile: parsers.conf add add new item logLevel: debug
save and the fluentbit will reload in about 10 seconds.
How to exclude certains logs
To excludes certain logs, we can utilize grep
For example lets create a configuration to skip logs from Namespace, create skip-namespace.yaml with following lines
apiVersion: fluentbit.fluent.io/v1alpha2 kind: ClusterFilter metadata: annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: fluent-operator meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: monitoring labels: app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm fluentbit.fluent.io/component: logging fluentbit.fluent.io/enabled: "true" name: skip-namespace spec: match: kube.* filters: - grep: exclude: $kubernetes['namespace_name'] kube-system
deploy it to Kubernetes
kubectl apply -f skip-namespace.yaml -n monitoring
Skip logs based on the container name
apiVersion: fluentbit.fluent.io/v1alpha2 kind: ClusterFilter metadata: annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: fluent-operator meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: monitoring labels: app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm fluentbit.fluent.io/component: logging fluentbit.fluent.io/enabled: "true" name: fluentbit-config-skip-namespace spec: match: kube.* filters: - grep: exclude: $kubernetes['pod_name'] fluent-bit
We don’t need to create multiple object to exclude the logs, we can combine them in the same file. For example see following example
spec: match: kube.* filters: - grep: exclude: $kubernetes['pod_name'] fluent-bit exclude: $kubernetes['namespace_name'] kube-system exclude: $kubernetes['namespace_name'] staging
Send the logs to Elasticsearch
Create a secret to store username and password for Elasticsearch, create a new file kubernetes-elasticsearch-secret.yaml, encode your username and password using base64. For example for username admin we can run command from Linux CLI
$ echo admin | base64 # output YWRtaW4K
copy the output and add it to the configuration file
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-secret
namespace: monitoring
data:
username: YWRtaW4K
password: U3VQM3JTM0NyM3RBZG1pbgo=then deploy it to the cluster
kubectl apply -f kubernetes-elasticsearch-secret.yaml -n monitoring
The create another configuration to enable Elasticsearch/Opensearch, kubernetes-elasticsearch.yaml
apiVersion: fluentbit.fluent.io/v1alpha2 kind: ClusterOutput metadata: annotations: meta.helm.sh/release-name: fluent-operator meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: monitoring labels: app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm fluentbit.fluent.io/component: logging fluentbit.fluent.io/enabled: "true" name: fluentbit-config-elasticsearch spec: es: bufferSize: 15MB host: elasticsearch.atetux.com port: 443 httpPassword: valueFrom: secretKeyRef: key: password name: elasticsearch-secret httpUser: valueFrom: secretKeyRef: key: username name: elasticsearch-secret index: prod replaceDots: true suppressTypeName: "true" tls: verify: false match: 'kube.*'
deploy it
kubectl apply -f kubernetes-elasticsearch.yaml -n monitoring
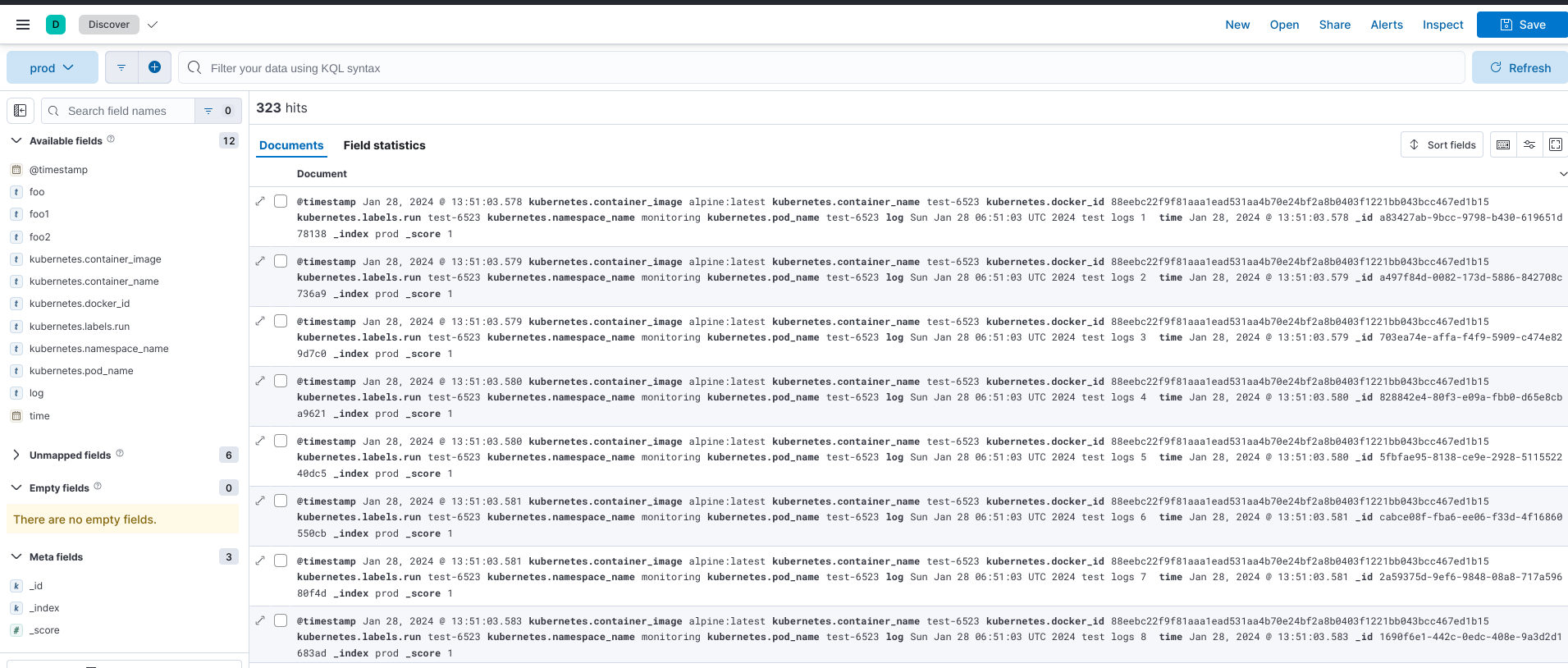
Generate Logs
To verify our configuration working, we need to generate some logs
kubectl run test-$RANDOM --namespace monitoring --image=alpine --command -- sh -c 'for i in $(seq 1 10); do echo "$(date) test logs $i"; done'
it’ll create alpine pod, and print some logs.
Then check the Elasticsearch the logs should coming