Systemd has built-in tools to manage time on Linux, which shipped in most Linux distro which uses systemd such as RHEL/CentOS, Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Archlinux. The timedatectl command allows you to change time, date, and timezone on Linux system.
In this tutorial, we’ll manage time in Linux by setting the date, time and timezone using timedatectl command. It’s a best practice to use the correct time on your Linux server to make troubleshooting or checking file log more easiers.
Get current Timezone
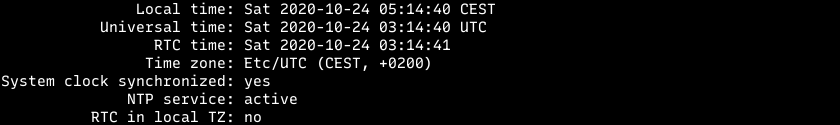
Using timedatectl command is straight forward, let’s get our current time and timezone
timedatectl status
To get list of known timezone, run following command
timedatectl list-timezones

To set timezone, use sub-command set-timezone, for example
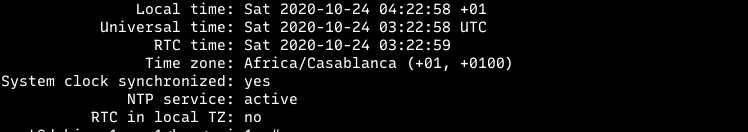
timedatectl set-timezone "Africa/Casablanca"the timezone will changes after that command executed, which can be verify using timedatectl status
Set timedatectl NTP Server
The best way to keep time synced and updated is using NTP (Network Time Protocol). The list of public NTP server can be found on ntppool.org
To enable NTP run following command
timedatectl set-ntp trueTo disable NTP
timedatectl set-ntp falseIf you notice we haven’t set the NTP server, to check the NTP server list used execute timedatectl show-timesync –all
LinkNTPServers= SystemNTPServers= FallbackNTPServers=0.debian.pool.ntp.org 1.debian.pool.ntp.org 2.debian.pool.ntp.org 3.debian.pool.ntp.org ServerName=2.debian.pool.ntp.org ServerAddress=2606:4700:f1::123 RootDistanceMaxUSec=5s PollIntervalMinUSec=32s PollIntervalMaxUSec=34min 8s PollIntervalUSec=34min 8s NTPMessage={ Leap=0, Version=4, Mode=4, Stratum=3, Precision=-26, RootDelay=48.583ms, RootDispersion=671us, Reference=A230E10, OriginateTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, ReceiveTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, TransmitTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, DestinationTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:29:02 +01, Ignored=no PacketCount=79, Jitter=322us } Frequency=607537
NTP server used by timedatectl stored at /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf file, change the NTP= line to
NTP=time.cloudflare.com time.google.com time.facebook.com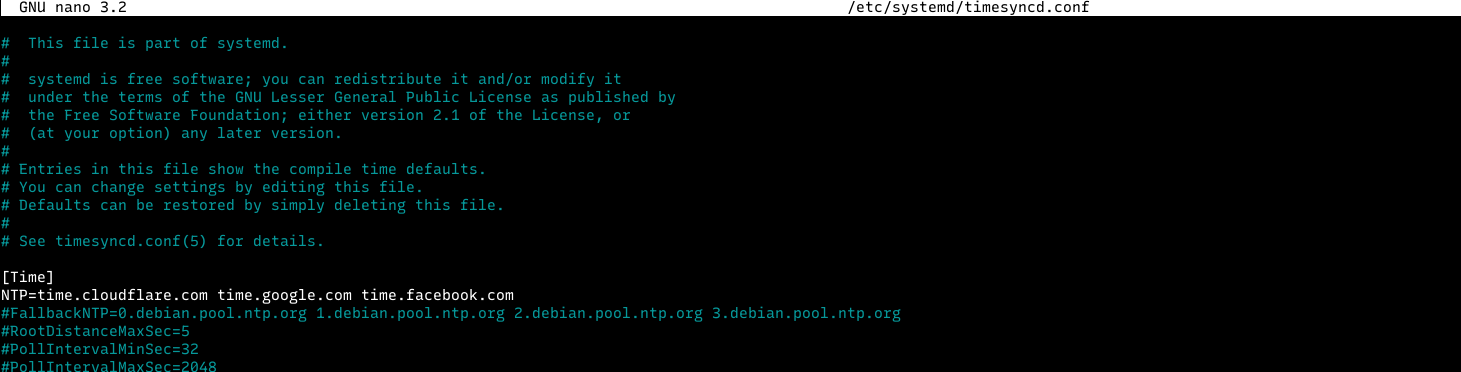
restart the systemd-timesyncd services to applied the changes
systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd.service
check the systemd service status
systemctl status systemd-timesyncd.service
Check the NTP server timedatectl show-timesync --all
LinkNTPServers= SystemNTPServers=time.cloudflare.com time.google.com time.facebook.com FallbackNTPServers=0.debian.pool.ntp.org 1.debian.pool.ntp.org 2.debian.pool.ntp.org 3.debian.pool.ntp.org ServerName=time.cloudflare.com ServerAddress=2606:4700:f1::1 RootDistanceMaxUSec=5s PollIntervalMinUSec=32s PollIntervalMaxUSec=34min 8s PollIntervalUSec=1min 4s NTPMessage={ Leap=0, Version=4, Mode=4, Stratum=3, Precision=-25, RootDelay=48.599ms, RootDispersion=534us, Reference=A230E10, OriginateTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, ReceiveTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, TransmitTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, DestinationTimestamp=Sat 2020-10-24 04:39:41 +01, Ignored=no PacketCount=1, Jitter=0 } Frequency=664177
The reason I prefer using a well-known company for NTP server because I notice some NTP server randomly disappear from internet, and the uptime under 90% in a month which unacceptable for production server.
This posts helped me to configure my laptop. I have recently upgrade to Debian trixie and my clock was always out of sync after a power off. Thank you for your tutorials, they are very instructive.