Load balancing is a common technique to make high availability, reliability, and scalability. When the application grows you’ll need to think a way to scaling the server to serve the visitor or customer better.
Nginx support few load balancing method which has its own advantages and disadvantages
1. Round Robin (default method)
Requests are distributed evenly across the servers
2. Least Connections
The request is sent to the server with the least connection.
3. IP Hash
The server served to depend on the client IP address.
4. Generic Hash
determined from a user‑defined key
Prerequisites
A server with Debian 10 latest version.
1 NGINX Server
2 or more Application Server
even we only use a single Nginx for load balancing, in the production you’ll need at least 2 servers to act as load balancer.
In this case, we’ll not talk about the install application server, you can install a replica the server with a similar setup. It is out of this tutorial scope
Setup DNS
The visitor will access the website through the frontend (in this case is Nginx), set the Nginx to your domain name

DNS propagation might take up to 24 hours after updated. Verify with dig tools on Linux or Mac
dig +short domain.comit should return the IP address of load balancer.
Install Nginx
Install the latest Nginx version provided by Debian 10
sudo apt install nginx -y
once installed, verify Nginx working by open the server IP address on the browser.
Configuring Nginx Load Balancing
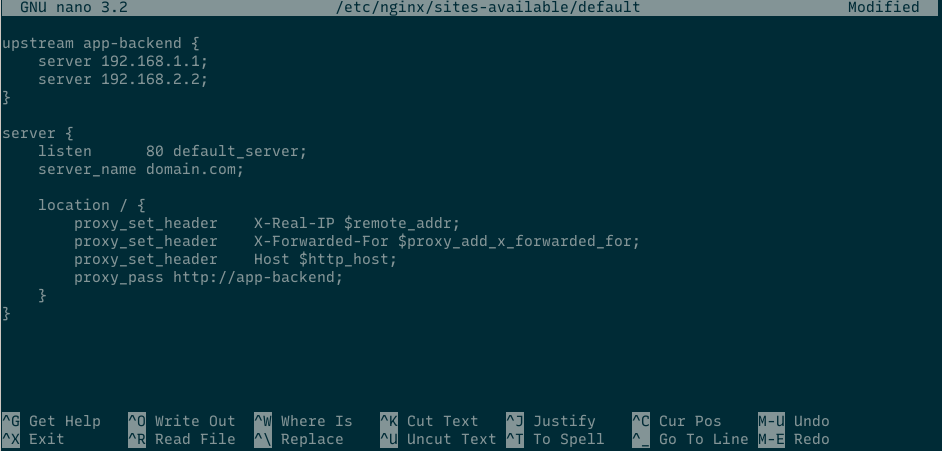
Default nginx server block stored at /etc/nginx/sites-available/default, we’ll use that file for our load balancer setup. Replace the content with
upstream app-backend { server 192.168.1.1; server 192.168.2.2; } server { listen 80 default_server; server_name domain.com; location / { proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_pass http://app-backend; } }
replace 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2 with the application server, if the application run on port other than 80, append on the end of IP, for example 192.168.1.1:8000
reload Nginx services
systemctl restart nginx
run Nginx after reboot
systemctl enable nginxTesting Load Balancing
The easiest way to check the load balancer working is using the browser
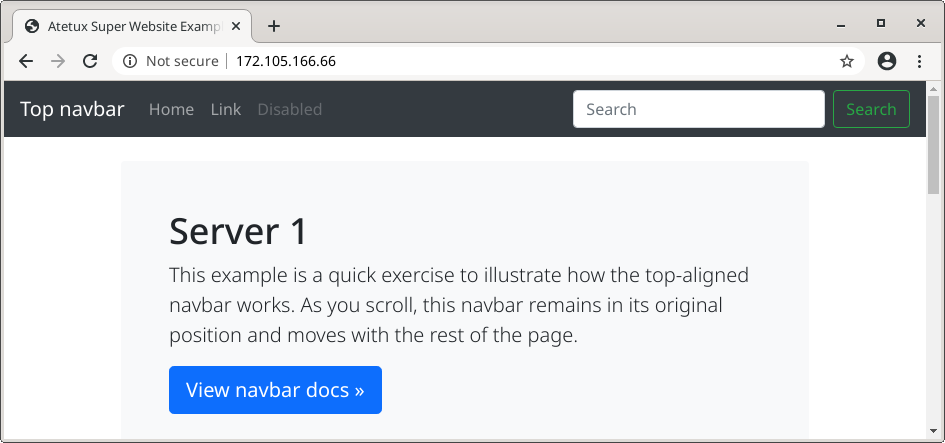
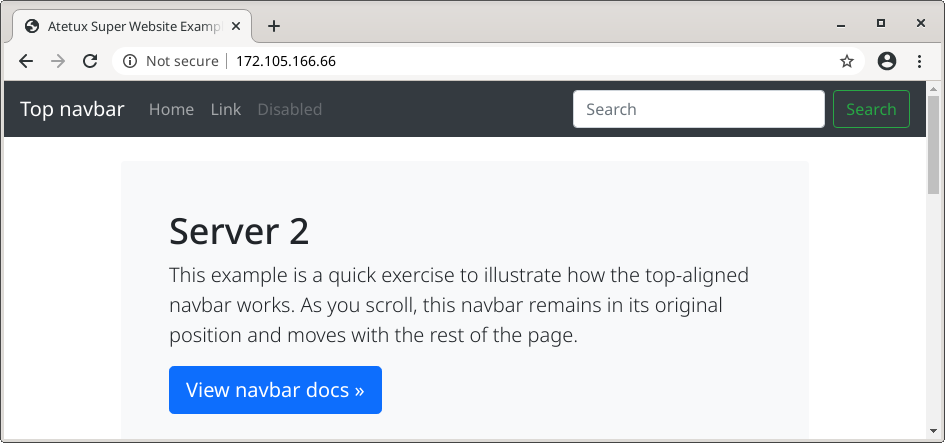
refresh few times. Another way is using old schoold curl
for i in {1..10}; do curl -s "http://domain.com/" ; done
it’ll open domain.com 10 times.
Load Balancing Method/Algorithm
To use one of the load balancing methods change the upstream block, because the round-robin is the default method we don’t need to add anything to the configuration. So we’ll add the other three.
1. Least Connections
upstream app-backend { least_conn; server 192.168.1.1; server 192.168.2.2; }
2. IP Hash
upstream app-backend { ip_hash; server 192.168.1.1; server 192.168.2.2; }
3. Generic Hash
upstream app-backend { hash $request_uri consistent; server 192.168.1.1; server 192.168.2.2; }